Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-14 Origin: Site








LED lighting has become the go-to choice for modern-day lighting solutions. Their energy efficiency and long lifespan make them popular for both commercial and residential applications. However, like any technology, LEDs can face issues over time. Understanding common problems and how to fix them ensures that LED systems remain functional and efficient for years to come.
In this article, we will explore common LED maintenance challenges and provide solutions to keep your systems running smoothly. You'll learn troubleshooting tips, preventive maintenance practices, and when it's time to call in a professional.
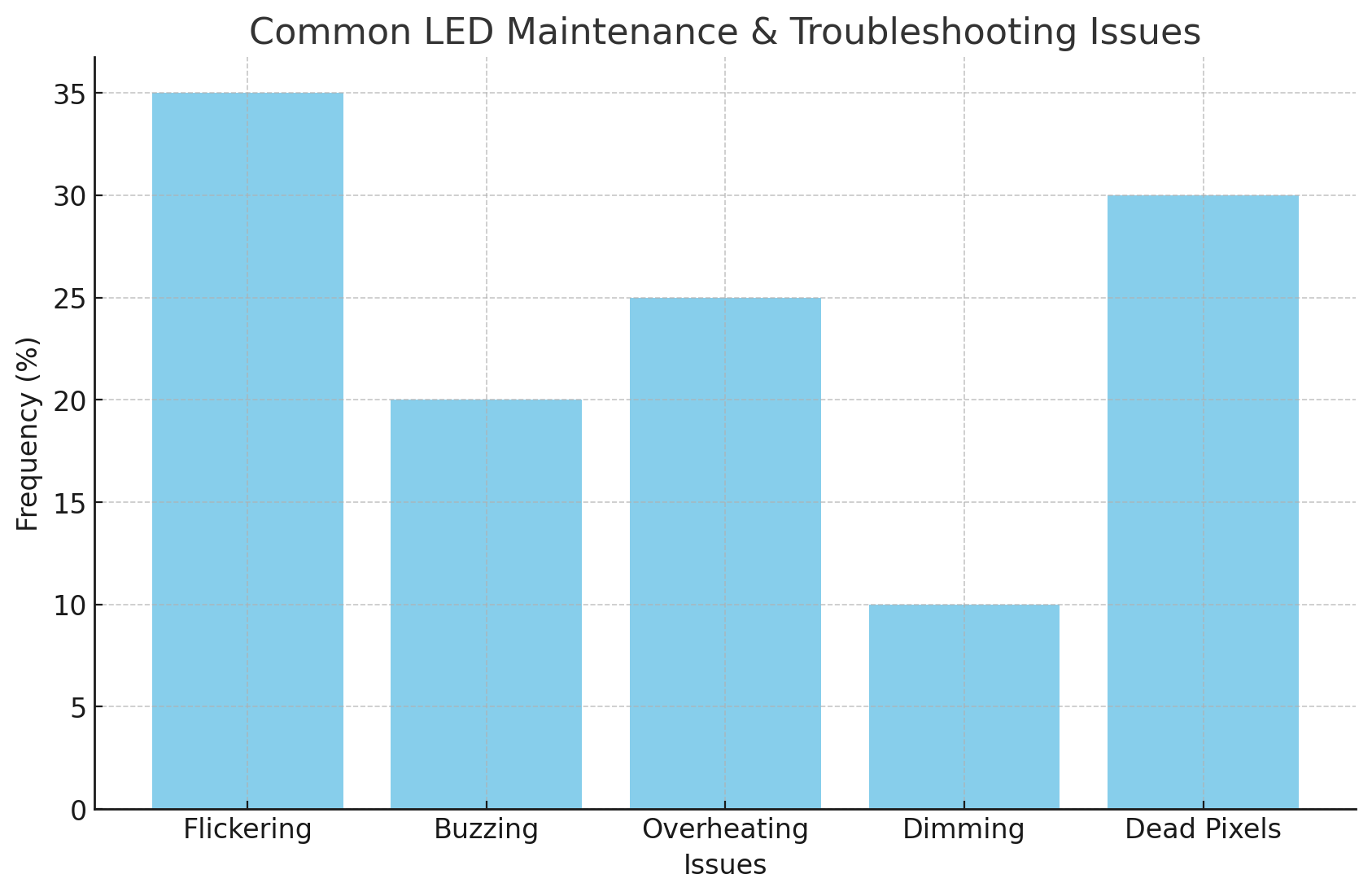
One of the most frequent problems with LED lights is flickering. This can occur due to several factors, such as power fluctuations or using an incompatible dimmer switch. In some cases, a faulty driver or loose wiring can cause the lights to flicker intermittently. To resolve this, ensure that the dimmer switch is LED-compatible and check the power supply for consistency. Replacing a faulty driver or stabilizing the wiring will also prevent flickering. In addition, consider investing in LEDs with built-in flicker-free technology for a smoother experience.
Buzzing noises in LED lighting systems are typically caused by incompatible dimmer switches or issues with the LED drivers. When LED lights are paired with dimmers that are not designed for LEDs, the power fluctuations can result in humming sounds. To fix this, replace the dimmer switch with one specifically made for LED lights. If the issue persists, it may be necessary to replace the driver, ensuring it matches the specifications for the LEDs being used.
Issue | Cause | Fix | Tools Needed |
Flickering Lights | Power fluctuations, incompatible dimmer switches | Stabilize power supply, use compatible dimmer | Multimeter, Dimmer Switch |
Buzzing or Humming | Faulty drivers, improper dimmer compatibility | Replace dimmer switch, or replace faulty drivers | Screwdriver, Multimeter |
Overheating | Inadequate ventilation or improper installation | Improve ventilation, use heat sinks | Screwdriver, Heat Sink |
LED Light Dimming | Aging LEDs, poor power supply | Replace aging LEDs, ensure proper voltage | Multimeter, Replacement LEDs |
Although LEDs generate less heat than incandescent bulbs, they can still overheat if not installed properly or if there is insufficient airflow. Overheating can lead to reduced lifespan and potentially damage the LEDs. To prevent this, ensure proper ventilation around the LEDs and use fixtures designed to dissipate heat effectively. If the LEDs are placed in a confined space, consider adding heat sinks or improving airflow to maintain optimal temperature levels.
LEDs may start to dim over time, which can be caused by aging components or an insufficient power supply. Inadequate voltage or a low-quality power source can result in poor light output. To address dimming, check the power supply to ensure that the LEDs are receiving the correct voltage. Additionally, replacing aging LEDs or upgrading to a higher-lumen version can help restore the brightness to its original level.
If an LED light is not turning on at all, the issue could be with the power supply, the LED itself, or the wiring. Start by checking the power supply to ensure that it is delivering the correct voltage. If the power supply is functioning correctly, inspect the wiring for loose connections or damage. If the LED light still doesn’t work, the LED itself may be faulty and require replacement.
In the case of LED displays, dead or stuck pixels are common problems. These can occur due to manufacturing defects or physical damage to the LED panel. To fix this, inspect the pixel area carefully. Stuck pixels can sometimes be revived using software tools like JScreenFix, while dead pixels usually require replacing the affected module or LED. Regular maintenance and ensuring a secure installation will prevent such issues from arising frequently.
Color inconsistencies in LED lights or displays can be caused by factors like voltage fluctuations or driver malfunctions. If some areas of the display appear dimmer or show incorrect colors, the driver may be failing or the LEDs may not be receiving stable power. To fix this, inspect the power supply and replace any faulty components. Ensure that the LEDs are all connected properly and check the calibration settings on the control panel if applicable.
Signal and power supply issues can lead to LEDs not responding correctly or displaying images inconsistently. Common causes include faulty wiring or malfunctioning power supplies. Troubleshooting these issues involves testing the power supply with a multimeter to check for consistent output. Additionally, check all wiring connections for stability and ensure that the signal input is working correctly. If any of these components are malfunctioning, they should be replaced to restore normal LED functionality.
Performing regular inspections of LED lights and displays is crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate. This includes checking for dust buildup, inspecting wiring, and ensuring the proper operation of all components. A routine inspection schedule should include cleaning the lights, tightening loose connections, and ensuring that all LEDs are functioning correctly.
Environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity can greatly affect the performance of LED lights. LEDs installed in areas with high humidity or extreme temperature fluctuations may fail prematurely. To mitigate this, ensure that the LEDs are housed in suitable enclosures and avoid placing them in environments that exceed their rated conditions. For outdoor LED lights, consider using fixtures rated for exposure to harsh weather conditions, such as those with an IP65 rating or higher.
Many modern LED systems feature smart capabilities that rely on software to manage functions like brightness, color temperature, and performance. Keeping firmware updated is essential to ensure that the LED system operates at peak efficiency. Software updates often include bug fixes, performance enhancements, and security improvements that prevent technical issues from affecting the display. Regularly check for updates and install them as needed to maintain optimal LED performance.

LED displays may fail to turn on or become non-responsive for a variety of reasons, including power supply issues, signal interruptions, or malfunctioning components. To troubleshoot this, start by checking the power supply and ensuring all connections are intact. If the power supply is stable and the wiring is secure, test the signal input to rule out issues with the source. If none of these steps resolve the problem, the display’s control board or driver may need to be replaced.
Localized blackouts or missing color blocks on an LED display can be caused by a malfunctioning module, power issues, or faulty signal transmission. Begin by inspecting the affected area and checking the connections between the LED modules. If the power supply is working correctly, test the signal input and replace any damaged modules. Adjusting the display settings may also help resolve color block issues.
Inconsistent brightness or flickering on LED displays can result from a range of factors, including unstable power, driver issues, or aging LEDs. To address this, check the power supply to ensure stable voltage. Inspect the driver for faults and replace it if necessary. Additionally, ensure that the display is properly calibrated and that the LEDs are not overheating.
A variety of tools are necessary for effective LED maintenance and troubleshooting. Some of the most important include:
● Multimeters for measuring voltage and resistance.
● Screwdrivers for disassembling LED fixtures and modules.
● Soldering irons for repairing connections and replacing components.
Each tool plays a critical role in diagnosing and fixing LED problems. Multimeters help identify power issues, screwdrivers allow for module access, and soldering irons are essential for repairing faulty connections.
Tool | Purpose | Use Case |
Multimeter | Measures voltage, current, resistance | Testing power supply, checking driver output |
Soldering Iron | Used for replacing LED components | Replacing damaged LED beads |
Thermal Camera | Measures temperature distribution | Identifying overheating issues |
Oscilloscope | Visualizes voltage fluctuations | Checking signal integrity and power supply issues |
Digital Thermometer | Measures LED temperature | Testing heat dissipation |
For more advanced diagnostics, tools such as thermal cameras, oscilloscopes, and insulation resistance testers are invaluable. Thermal cameras help identify hot spots caused by overheating, while oscilloscopes are used to analyze signal behavior and power issues. Insulation resistance testers ensure that the LED system is properly grounded and safe from electrical faults.
LED Issue | Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Process | Tools Required |
No Illumination | Check power supply, test wiring, and inspect LEDs | Multimeter, Screwdriver |
Dead or Stuck Pixels | Check signal cables, inspect modules, replace cables | Multimeter, Soldering Iron |
Inconsistent Color Output | Verify driver functionality, check voltage levels | Multimeter, Oscilloscope |
Flickering Displays | Inspect power supply and check dimmer compatibility | Multimeter, Dimmer Switch |
While many LED issues can be fixed with basic troubleshooting, complex hardware failures may require professional expertise. If you encounter issues like signal processing board failures, custom firmware problems, or severe damage to the LED panels, it’s best to consult with a professional. Attempting to fix these issues without proper knowledge can lead to further damage.
If your LED system is still under warranty, it’s advisable to take advantage of the coverage for repairs or replacements. Many LED manufacturers offer warranties that cover parts and labor for a specific period. Professional repair services can also provide in-depth diagnostics and efficient solutions, saving you time and money on repairs.
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for the longevity of LED systems. Regular inspections help address common issues like flickering and overheating, ensuring optimal performance. Using the right diagnostic tools is essential for maintaining LED systems. For those uncertain about repairs, consulting professionals is advisable to prevent costly mistakes and extend the system's lifespan.
At Guangzhou Zongheng Technology, we provide reliable LED solutions designed for longevity and efficiency, ensuring your lighting systems perform at their best.
A: Flickering in LED lights is often caused by power fluctuations or incompatible dimmer switches. Proper LED Maintenance & Troubleshooting ensures flickering issues are resolved by stabilizing the power supply and using compatible dimmer switches.
A: Overheating occurs due to poor ventilation or improper installation. Effective LED Maintenance & Troubleshooting includes ensuring proper airflow and using heat management systems like heat sinks.
A: Tools like multimeters, screwdrivers, and soldering irons are crucial for diagnosing LED issues. For advanced LED Maintenance & Troubleshooting, a thermal camera and oscilloscope can help pinpoint problems quickly.
A: LED lights may not turn on due to issues like power supply failure or dead LEDs. In this case, perform a thorough LED Maintenance & Troubleshooting check to identify the root cause and replace faulty components.
A: Color inconsistencies are often caused by driver failure or voltage fluctuations. Proper LED Maintenance & Troubleshooting helps by identifying these issues and replacing the faulty components or adjusting voltage levels.